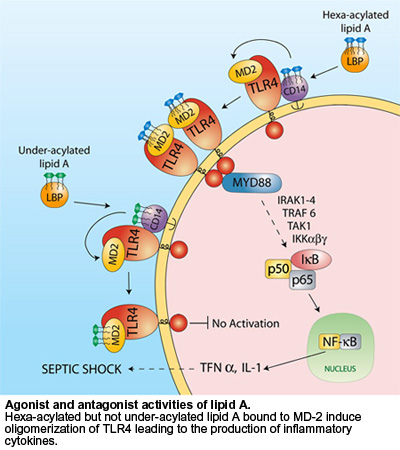
Effect of TLR4 inhibitors on proliferation of A549 cells during 24 h in... | Download Scientific Diagram

Insights into the species-specific TLR4 signaling mechanism in response to Rhodobacter sphaeroides lipid A detection | Scientific Reports
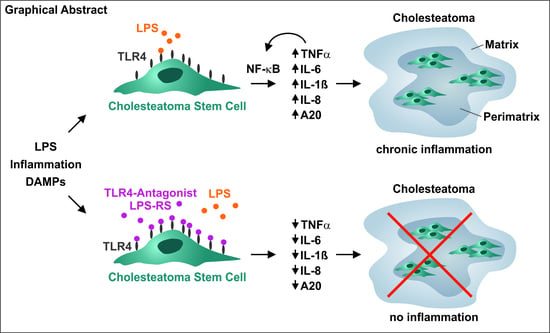
Cells | Free Full-Text | Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS

Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein-Induced Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signaling Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonists Rhodobacter sphaeroides Lipopolysaccharide and Eritoran (E5564) and Requires Direct Interaction with MD-2 | mBio
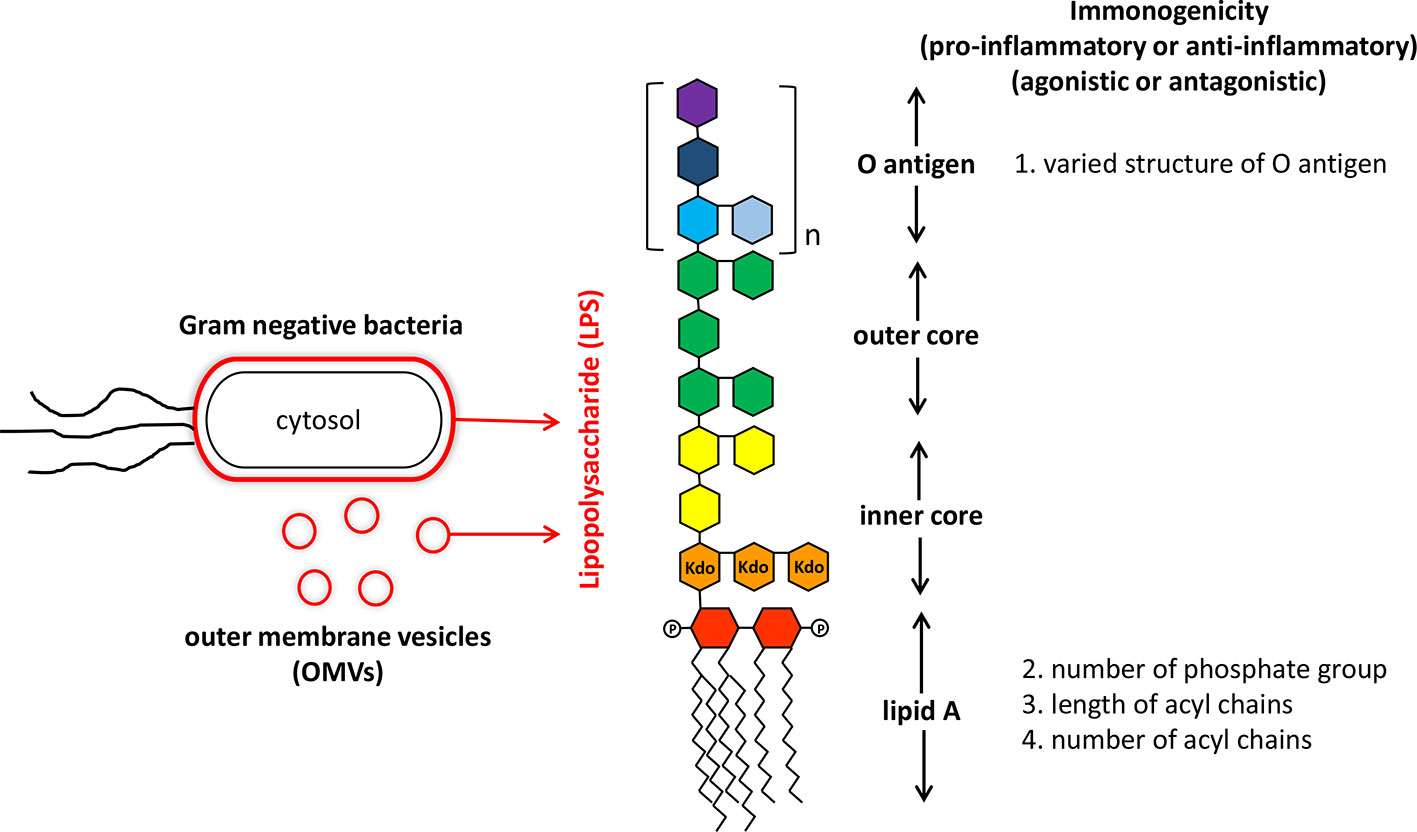
Frontiers | Like Cures Like: Pharmacological Activity of Anti-Inflammatory Lipopolysaccharides From Gut Microbiome

Conformationally Constrained Lipid A Mimetics for Exploration of Structural Basis of TLR4/MD-2 Activation by Lipopolysaccharide | ACS Chemical Biology
Identification of Key Residues That Confer Rhodobacter sphaeroides LPS Activity at Horse TLR4/MD-2 | PLOS ONE

Pharmaceuticals | Free Full-Text | Therapeutic Targeting of TLR4 for Inflammation, Infection, and Cancer: A Perspective for Disaccharide Lipid A Mimetics

Limonin Attenuates LPS-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Pyroptosis via NLRP3/Gasdermin D Signaling Pathway | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Kdo2‐lipid A: structural diversity and impact on immunopharmacology - Wang - 2015 - Biological Reviews - Wiley Online Library
Lipopolysaccharide Induces Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and MMP Production via TLR4 in Nasal Polyp-Derived Fibroblast and Organ Culture | PLOS ONE
Research Article Lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter sphaeroides Attenuates Microglia-Mediated Inflammation and Phagocytosis and

Both LPS and MPLA activate human adherent mononuclear cells via TLR4.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Both LPS and MPLA activate human adherent mononuclear cells via TLR4.... | Download Scientific Diagram
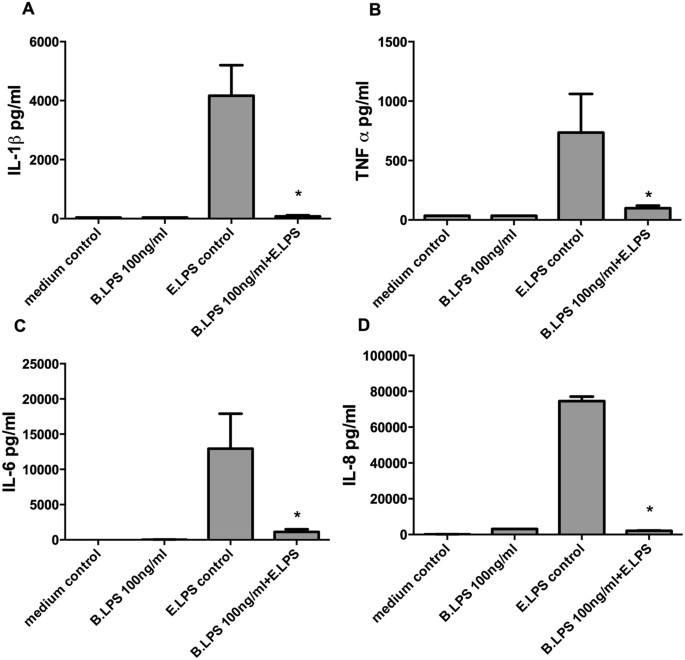
Bartonella quintana lipopolysaccharide (LPS): structure and characteristics of a potent TLR4 antagonist for in-vitro and in-vivo applications | Scientific Reports

IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Role of Carbohydrates in the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signalling
Identification of Key Residues That Confer Rhodobacter sphaeroides LPS Activity at Horse TLR4/MD-2 | PLOS ONE